Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
This is a brownfield project that bases from the Project template AddressBook Level 3 (AB3) from se-education.org.
Setting up, getting started
Get started by following these instructions from our guide.
Design
Take a look at our design which is mostly based off AddressBook Level 3 (AB3).
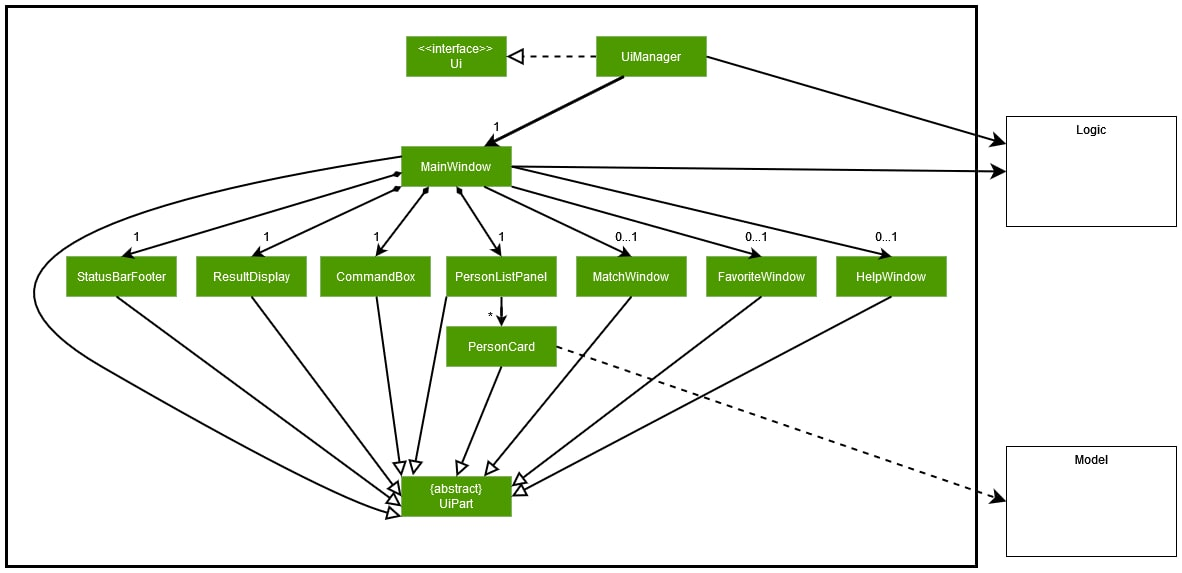
##Architecture
##UI Component
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Favourite feature and Favourites window
The proposed favourite mechanism will make use of a new attribute called Favourite. How we went about creating this mechanism is by going through the list of Persons and checking if their Favourite instance returns “🌟” (represents favourited) when toString() is called.
Given below is an example of how the favourite mechanism behaves with the Favourites window.
Step 1. The user starts the application with pre-loaded data of Persons.
Step 2. Assuming there is a Person with the index number 1. User then executes favourite 1 command to favourite the Person with index number 1 in the application. The system will create a new Person with the Favourite instance’s value set as true. Then calls Model#setPerson() to set this Person to be a favourited instance of the same Person.
Step 3. User can access the Favourites window by navigating to the menu item as shown in the diagram, which pops up a new window that contains only those Persons that have ‘Favourite’ instance’s value set as True. The user can also input the command fw to open up the Favourites window through this CLI command.
Match feature/Window
The match opens a new MatchWindow, in which all matches are displayed in pairs.
The left column shows the sellers, while the right column shows the buyers.
Two Person make a match if the seller has at least one property that matches the buyer’s preference.
Help Feature and Window
The help command and selecting help from the dropdown opens the helpwindow.
The contents of helpPanePlaceHolder is then replaced according to which tab
that the user has selected to view more details about a specific feature or general features
of Realestatepro
Property
The Property is a new attribute that can be added to a Person that represents a real estate property listing. A Person is able to hold multiple properties including none.
The Property itself consists of the following attributes: Region, Address, Size, Price.
-
Regionrepresents the general location of theAddressof theProperty. It is an enum that can be one of the following:NORTH,SOUTH,EAST,WEST,CENTRAL. -
Addressrepresents the exact location of theProperty. -
Sizerepresents the size of thePropertyin terms of the number of rooms it has. It is an enum that can be one of the following:ONE_ROOM,TWO_ROOM,THREE_ROOM,FOUR_ROOM,FIVE_ROOM. -
Pricerepresents the price of theProperty. It’stoString()method returns the price in the form of$###or$###.#Kor$###.#Mdepending on the value of thePricefor easier readability.
Preference
The Preference is a new attribute that can be added to a Person. A Person can either have a Preference or none.
A Preference contains the following attributes: Region, Size, lowPrice, highPrice,
among which the first two is explained in the previous segment.
The latter two specifies the expected range of money the buyer would like to pay for a property.
UserType
The UserType represents an attribute that is added to a Person & can represent the Person as a buyer or seller. A Person is only either a buyer or seller at a given time. They cannot be both or none. The UserType of a Person is derived from the presence of a Property or Preference. If the Person has a Property, then they are a seller, but if the Person has a Preference, then they are a buyer.
Unlike other attributes of a Person, the UserType of a Person cannot be edited directly via the edit command. A Person can be changed from a buyer to a seller & vice versa if the Person’s property or preference is changed. This can be done with the command: edit INDEX pr/PROPERTY_DETAILS or edit INDEX pf/PREFERENCE_DETAILS. This means editing a Person to have a Property instead of a Preference will change them from a buyer (had a Preference initially) to a seller (now has a Property). In other cases where other attributes of a Person are being edited, e.g. phone number, address, the UserType of that Person being edited will remain the same.
Remind feature
The remind feature is implemented by storing a static list of Persons the user wants to be reminded of.
ReminderTask– Schedules and handles the work of activating the Reminders window.ReminderPersons– Stores aHashSetofPersons, because only 1 reminder can be set per person & thus only 1 occurrence of a Person in this data structure is allowed.ReminderWindow– A Window to display allPersons the client set reminders for.- Both
ReminderTaskandReminderWindowclasses are singletons as there can only ever be 1 occurrence of these classes.
The remind feature can be activated by typing remind INDEX r/ReminderDetails where INDEX is the Person the user wants to set a reminder for and ReminderDetails are the details of the reminder in regard to the specific client.
Given below is an example usage scenarios and the behavior of the program specific to this feature.
Step 1: The user launches the app. Within 5 seconds, a Reminder window pops up & displays any reminders the user has actively set. As the User does not have any active reminders set, they can add a reminder.
Step 2: User executes the remind command by typing in remind 1 r/arrange meeting, as the user wants to set a reminder for the client with Index 1. The RemindCommandParser parses the Index the User inputted & creates a RemindCommand. The RemindCommand is executed & retrieves the Person corresponding to the Index from Model. This Person and the corresponding Reminder is then added to the HashMap in ReminderPersons. The CommandResult returned is created with the input argument showReminders marked as true. This then gets executed by MainWindow and the ReminderWindow is launched.
Step 3: The User will be prompted with the Reminder window, containing the Person the user just set a Reminder for.
Step 4: The User can continue using the app, but after a minute since the Reminder window last popped up, the Reminder window launches again to actively remind the User of any reminders.
Upload Image
The upload image feature is implemented by storing a set of UserImage containing
a FilePath to an image file and an optional description of the image. A LinkedHashSet is utilized
to retain order based on the order of insertion.
UserImage– Contains all information needed to display the image that is associated with the PersonFilePath– Leads to a file that is located in the user’s system
There are two commands that are associated with this feature, namely upload and viewimage.
Below is an example usage scenario and the behaviour of the program:
Step 1: User calls the upload command.
UploadCommandParser would then be used to parse the command inputted to obtain the index of the Person to add
the image with, the filepath to the file (the validity of the file is checked) and
the description if provided.
Step 2: A UserImage is created from the parameters obtained from UploadCommandParser that checks to ensure that the
file FilePath provided is an image before adding it to the
Person.
Step 3: User calls the viewimage command that ViewImageCommandParser parses to get the index of the Person to
view all the UserImage of the Person.
Step 4: The set of UserImage is then passed to model via model#updateViewPerson(Set<UserImage>).
The viewImageWindow is then launched after it retrieves the set from model
Step 5: The set of UserImage is then converted into an ArrayList and the first image is displayed in the window.
Statistics feature/Window

The stats opens a new StatisticsWindow that displays a pie chart with the data of the number of sellers & buyers in the 5 different regions, namely {North, South, East, West, Central}.
This allows the user to be able to visualize his/her client’s data to make better business decisions. (exp. Expand the user’s influence in the most popular region for any potential sellers/buyers to contact him/her)
[Future version] </br> Displaying statistics of the number of properties being sold/bought categorized by their room size to provide insight on the most popular number of rooms in a property. Displaying statistics of the prices of properties sold/bought to provide insight on the average property price sold/bought. Displaying statistics of lower price and higher price of preferences of clients to provide insight on the average asking price of a property.
Sorting
The sorting feature allows the user to sort the list of Person displayed.
The following table shows the attributes that the list can be sorted by and their corresponding keywords.
| Attribute | Keyword |
|---|---|
Name |
name |
Phone |
phone |
Email |
email |
Favourite |
favourite |
Address |
address |
UserType |
usertype |
Number of Property |
num_property |
Sorting the list is done by using the sort command, which has the following syntax: sort [KEYWORD]....
If multiple attributes are specified, the first attribute is given the highest priority, while the last attribute is given the lowest priority. For example, sort address name will sort the list by Address first, followed by Name if Address is equal.
The sorting feature is implemented by using a SortedList<Person> to observe the FilteredList<Person> in ModelManager.
Whenever the underlying application data is modified, the FilteredList<Person> is notified first and will filter the data. If there is any change in the FilteredList<Person>, the SortedList<Person> is notified and will sort the filtered data.
Feature find enhanced
In addition to the original NameContainsKeywordsPredicate, more predicates concerning each of the attributes in a Person are created.
They can be fed to the FindCommand to filter out Person with the specified keywords in the specified attribute.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
This is how we do our documentation.
This is how we do our testing.
This is how we do our logging.
This is how we do our configurations.
This is how we do our DevOps.
Appendix: Requirements
Target user profile
- has a need to manage a significant number of Persons and their information (eg. contact, email, address…)
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast and prefer typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value Proposition
Manage Persons faster that a typical mouse/GUI driven app.
User stories
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that i can… |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | User | Delete my client’s information on the app | Remove this redundant information after he/she is not my client anymore |
| High | User | To edit my clients’ information on the app | Ensure all information of my clients are always up to date |
| High | User | To list out my clients’ information on the app | View all of my clients’ information in one place |
| High | User | Differentiate my clients’ on the app (e.g. buyers, sellers) | Know if a client is looking for a property to buy or is trying sell a property |
| High | User | Add my clients’ information on the app | Gain access to all these information in one place |
| High | User | Favourite a client | Separate clients based on whose information I frequent the most (favourited) and those that are not |
| High | User | View favourited clients | Have a compact display of clients that I frequent the most |
| High | User | To create a preference for a client who is a buyer | Have information of potential properties that the buyer would want to buy |
| High | User | Match my clients (e.g. buyer with seller) | Spot if there are any properties being sold by a seller that a buyer has a preference for. |
| High | User | Be able to understand how the app works from start to end | Able to provide the necessary inputs to perform a particular action on the app |
| High | User | display data of the number of sellers & buyers based on the particular region that the seller has properties in or the buyer having a preference of when looking to buy properties | Be able to make the better business decision to look for more clients in the most popular region |
Use cases
Non-functional Requirements
- Should be able to work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 or above installed
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- No lag of more than one second when executing commands
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 Persons without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- The application will not be able to prevent any data privacy violated by other programs.
Glossary
Buyer - client that is looking to buy a property based on some preference
Seller - client that is looking to sell a property for a particular price
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
- Initial launch
- Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
- Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
- Saving window preferences
- Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
- Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
- Shutting down
- First way you can do it is to click on the X button on the application.
- Another way is to click on ‘File’ menu item and click on ‘Exit’.
- Lastly, you can enter the
exitcommand.
Deleting a Person
- Deleting a Person while all Persons are being shown
- Prerequisites: List all Persons using the
listcommand. Multiple Persons in the list. - Test case:
delete 1Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. - Test case:
delete 0Expected: No Person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. - Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size or smaller than 0)Expected: Similar to previous.
- Prerequisites: List all Persons using the